The Difference Between Natural Black Diamonds and a Lab Created Ones
Natural Black Diamonds
A black diamond, also known as a “carbonado,” is a unique type of diamond that differs in appearance and composition from traditional white or colorless diamonds. Their dark black or dark gray color characterizes black diamonds, which is due to numerous microscopic black or dark inclusions within the diamond’s structure. These inclusions scatter light, giving black diamonds their distinctive opaque appearance.
Unlike white diamonds, which are composed of pure carbon, black diamonds are believed to have originated from a different process. They are thought to have formed from impact events, such as meteorite strikes, that subjected the carbon-containing material to immense heat and pressure, resulting in the unique composition and appearance of black diamonds.
Black diamonds are relatively rare and typically found in only a few locations around the world, including Brazil and Central Africa. They have gained popularity in recent years as unique and fashionable choices for jewelry, including rings, earrings, and pendants, due to their distinctive appearance and unconventional appeal. Black diamonds are also sometimes used in industrial applications due to their hardness and durability.

Lab Created Black Diamonds
Artificially made black diamonds, also known as “treated” or “enhanced” black diamonds, are diamonds subjected to various treatments or enhancements to alter their color and appearance. These treatments are done using high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) processes or through irradiation techniques.
HPHT-treated black diamonds are created by subjecting natural white or light-colored diamonds to intense heat and pressure, which causes the diamond to absorb and trap graphite or other dark inclusions, resulting in a black or dark gray color. This process mimics the natural formation of black diamonds believed to have formed from impact events.
Irradiation is another method used to create black diamonds artificially. Diamonds are exposed to high-energy radiation, such as electron beams or neutron bombardment, which alters their crystal lattice structure and can lead to a black color.
It’s important to note that treated black diamonds are different from natural black diamonds in terms of their value and rarity. Natural black diamonds are extremely rare and valuable, while treated black diamonds are generally less valuable due to their altered or enhanced nature. Treated black diamonds should always be disclosed as such when sold or used in jewelry to ensure transparency and accuracy in the market.

Why did the Diamond Industry Start Creating Black Diamonds?
The diamond industry started creating black diamonds through artificial treatments or enhancements, primarily to meet the growing demand for black diamond jewelry in the market. Black diamonds have gained popularity in recent years due to their unique and unconventional appearance, making them sought after for use in jewelry such as rings, earrings, and pendants.
Natural black diamonds are extremely rare and are found in limited quantities in only a few locations around the world, which makes them expensive and hard to obtain. As a result, the diamond industry turned to artificial treatments and enhancements to create black diamonds that could be more readily available and affordable for consumers.
Artificially created black diamonds also offer more versatility in terms of shape, size, and consistency in color compared to natural black diamonds, which can vary greatly in these characteristics. This makes treated black diamonds more suitable for jewelry manufacturing and design purposes.
Additionally, advances in technology and diamond treatment techniques have enabled the creation of black diamonds with high quality and desirable characteristics, further driving the demand for these unique gems in the jewelry market.
It’s important to note that treated black diamonds should be disclosed as such when sold or used in jewelry to ensure transparency and ethical business practices in the diamond industry. Consumers should always ask for proper documentation and certifications from reputable sources when purchasing black diamonds, to ensure they are accurately represented and ethically sourced gemstones.

Do Lab Created Black Diamonds hold the same value as White Diamonds?
Lab-created black diamonds do not hold the same value as natural white diamonds. Natural white diamonds are formed deep within the Earth’s crust over millions of years through natural geological processes, and are considered rare and precious gemstones. Their value is typically determined by the “Four Cs“: carat weight, cut, color, and clarity, with natural white diamonds of higher carat weight, excellent cut, and minimal color and clarity characteristics commanding higher prices.
On the other hand, lab-created black diamonds are artificially created in controlled laboratory environments using high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) processes or irradiation techniques to alter the color of natural or synthetic diamonds. These treated or enhanced black diamonds are more affordable compared to natural white diamonds, as they are not as rare or precious. The value of lab-created black diamonds is typically based on the cost of production, which is generally lower than the cost of mining and processing natural diamonds.
It’s important to note that the value of lab-created black diamonds, like all diamonds, may vary depending on factors such as size, shape, color, and clarity. However, lab-created black diamonds are more affordable than natural white diamonds, and do not hold the same intrinsic or investment value.
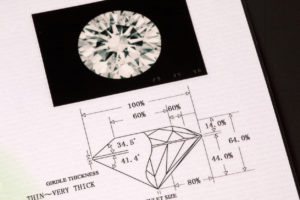
What is a Diamond Grading Report?
A diamond grading report, also known as a diamond certificate or diamond dossier, is a document issued by a gemological laboratory that provides an expert evaluation and detailed information about the quality and characteristics of a diamond. It is a vital tool for assessing the value and quality of a diamond, as it provides an independent, unbiased, and professional assessment of the diamond’s attributes.
A typical diamond grading report includes information such as:
Carat Weight: The weight of the diamond, usually expressed in carats, which is a unit of measurement for gemstones.
Cut: The quality of the diamond’s cut, including its proportions, symmetry, and polish, which affects the diamond’s ability to reflect light and create brilliance.
Color: The presence of any color in the diamond, ranging from colorless (graded as D) to faint or light yellow or brown (graded as Z), with grades based on a standardized scale.
Clarity: The presence of any internal or external characteristics, known as inclusions and blemishes, respectively, and their impact on the diamond’s clarity, graded on a scale from Flawless (FL) to Included (I1, I2, I3).
Shape and Measurements: The diamond’s shape, such as round, princess, or emerald, and its measurements, including diameter, depth, and table percentage.
Fluorescence: The diamond’s reaction to ultraviolet light, which may cause the diamond to emit a visible glow, graded on a scale from None to Very Strong.
Additional Information: Some grading reports may also include additional information, such as the diamond’s proportions, symmetry, and polish, as well as any other unique characteristics or features.
Reputable gemological laboratories issue diamond grading reports, such as the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), the American Gem Society (AGS), and the International Gemological Institute (IGI), among others. These reports serve as a valuable tool for consumers, jewelers, and insurers to accurately assess the quality and value of a diamond, and can be used for buying, selling, insuring, and appraising diamonds.

Do All Diamond Buyers Want a Diamond Grading Report When Selling Pre-owned Diamonds and Engagement Rings?
While it may vary depending on the specific circumstances and preferences of the diamond buyer, not all buyers may require a diamond grading report when purchasing pre-owned diamonds or engagement rings.
Some buyers may focus more on other factors, such as the overall design, style, craftsmanship, and brand of the jewelry, rather than the specific details of the diamond’s grading report.
However, many reputable and knowledgeable diamond buyers may request a diamond grading report as part of their due diligence process when evaluating pre-owned diamonds or engagement rings. A diamond grading report provides important information about the quality and characteristics of the diamond, helping the buyer assess its value and authenticity.
Having a diamond grading report can also add credibility and transparency to the selling process, as it provides an independent and professional assessment of the diamond’s attributes. It can help establish trust between the buyer and the seller, and provide confidence to both parties that the transaction is based on accurate and reliable information.
Furthermore, if you are selling a diamond or engagement ring with a diamond grading report from a reputable gemological laboratory, it can potentially command a higher price or attract more interest from buyers who value the additional information and assurance provided by the grading report.
It’s important to note that not all diamond grading reports are created equal, and the reputation and credibility of the gemological laboratory that issued the report can greatly impact its value and reliability.
Buyers may have their own preferences or requirements for the type of diamond grading report they accept. Therefore, it’s advisable to provide a diamond grading report from a reputable and recognized gemological laboratory to maximize the likelihood of meeting buyer expectations and achieving a fair transaction.

Can You Get a Quality Diamond from A Pawn Shop When You are Buying Diamonds?
Yes, it is possible to find quality diamonds at a pawn shop when buying diamonds. Pawn shops can be a source of pre-owned diamonds that are often sold at a discounted price compared to buying new diamonds from a traditional jewelry store. However, there are important factors to consider when purchasing diamonds from a pawn shop to ensure that you are getting a quality diamond.
Authenticity: It’s crucial to verify the authenticity of the diamond you are buying from a pawn shop. Requesting a diamond grading report from a reputable gemological laboratory can help confirm the diamond’s authenticity and provide information about its quality and characteristics.
Quality: Carefully assess the quality of the diamond based on the 4 Cs – carat weight, cut, color, and clarity. Consider the diamond’s appearance, brilliance, and any visible inclusions or blemishes. A diamond grading report can provide valuable information about these attributes.
Reputation of the Pawn Shop: Choose a reputable and established pawn shop with a history of dealing in diamonds and gemstones. Look for customer reviews, ratings, and feedback to gauge the credibility and reliability of the pawn shop.
Return Policy and Warranty: Inquire about the pawn shop’s return policy and warranty for diamonds. A reputable pawn shop may offer a reasonable return policy and provide a warranty or guarantee for the diamonds they sell, ensuring that you are satisfied with your purchase.
Price: Compare the price of the diamond at the pawn shop with market prices for similar diamonds of comparable quality. Consider factors such as the diamond’s condition, certification, and market demand when assessing the price.
Professional Appraisal: Consider getting a professional appraisal from a certified gemologist or independent appraiser to ensure you are getting a fair deal and a quality diamond.
It’s important to exercise caution and do your due diligence when buying diamonds from a pawn shop, just as you would when purchasing from any other source. Verifying the authenticity, quality, reputation of the pawn shop, return policy, and price are essential steps to ensure that you are getting a quality diamond that meets your expectations.

If You Live in Whittier, CA and the Surrounding Communities, is Lambert Pawn a Good Place to Buy Diamonds?
When considering whether a pawn shop is a good place to buy diamonds, it’s important to conduct your own research and due diligence. Here are some factors to consider:
Reputation: Research the reputation of Lambert Pawn in Whittier, CA, and the surrounding communities. Look for customer reviews, ratings, and feedback from reliable sources to gauge their credibility and reliability.
Expertise: Consider the expertise of the pawn shop in dealing with diamonds. Look for pawn shops that have a history of dealing in diamonds and gemstones, and have knowledgeable staff who can provide accurate information and guidance.
Authenticity: Inquire about the authenticity of the diamonds sold at Lambert Pawn. Ask about their process for verifying the authenticity of diamonds, and request diamond grading reports from reputable gemological laboratories to ensure the diamonds are genuine.
Quality: Assess the quality of the diamonds available at Lambert Pawn . Consider factors such as the 4 Cs – carat weight, cut, color, and clarity – and inspect the diamonds for any visible inclusions or blemishes.
Pricing: Compare the prices of diamonds at Lambert Pawn with market prices for similar diamonds of comparable quality. Consider factors such as the condition, certification, and market demand when assessing the prices.
Return Policy and Warranty: Inquire about the pawn shop’s return policy and warranty for diamonds. A reputable pawn shop may offer a reasonable return policy and provide a warranty or guarantee for the diamonds they sell, ensuring your satisfaction with the purchase.
Verify the reputation, expertise, authenticity, quality, pricing, return policy, and consider getting a professional appraisal to ensure that you are making a wise and informed purchase decision. Lambert Pawn will pass the test.

